Can Saw Palmetto Stop Hair Loss? Unpacking the Evidence
Can Saw Palmetto Stop Hair Loss? Unpacking the Evidence

Saw Palmetto (Serenoa repens) has garnered significant attention as a natural alternative for combating hair loss, particularly androgenic alopecia. Its appeal stems from its purported ability to act as a natural DHT blocker, a mechanism similar to some pharmaceutical treatments for hair thinning. This article delves into the science behind Saw Palmetto, examining what the research truly says about its effectiveness, how it might work, and what realistic expectations individuals should have when considering this botanical supplement for their hair health journey. We will explore the evidence, potential benefits, limitations, and how it stacks up against other hair loss interventions, providing a comprehensive, evidence-based perspective.
Understanding Androgenic Alopecia: The Root of Most Hair Loss
Before exploring Saw Palmetto, it's crucial to understand the most common form of hair loss it aims to address: androgenic alopecia (AGA). Often known as male or female pattern baldness, AGA affects millions globally, characterized by a progressive thinning of hair, leading to a receding hairline in men and diffuse thinning across the scalp in women. This condition is primarily genetic but is heavily influenced by hormonal factors, specifically androgens.
The Role of DHT in Hair Loss
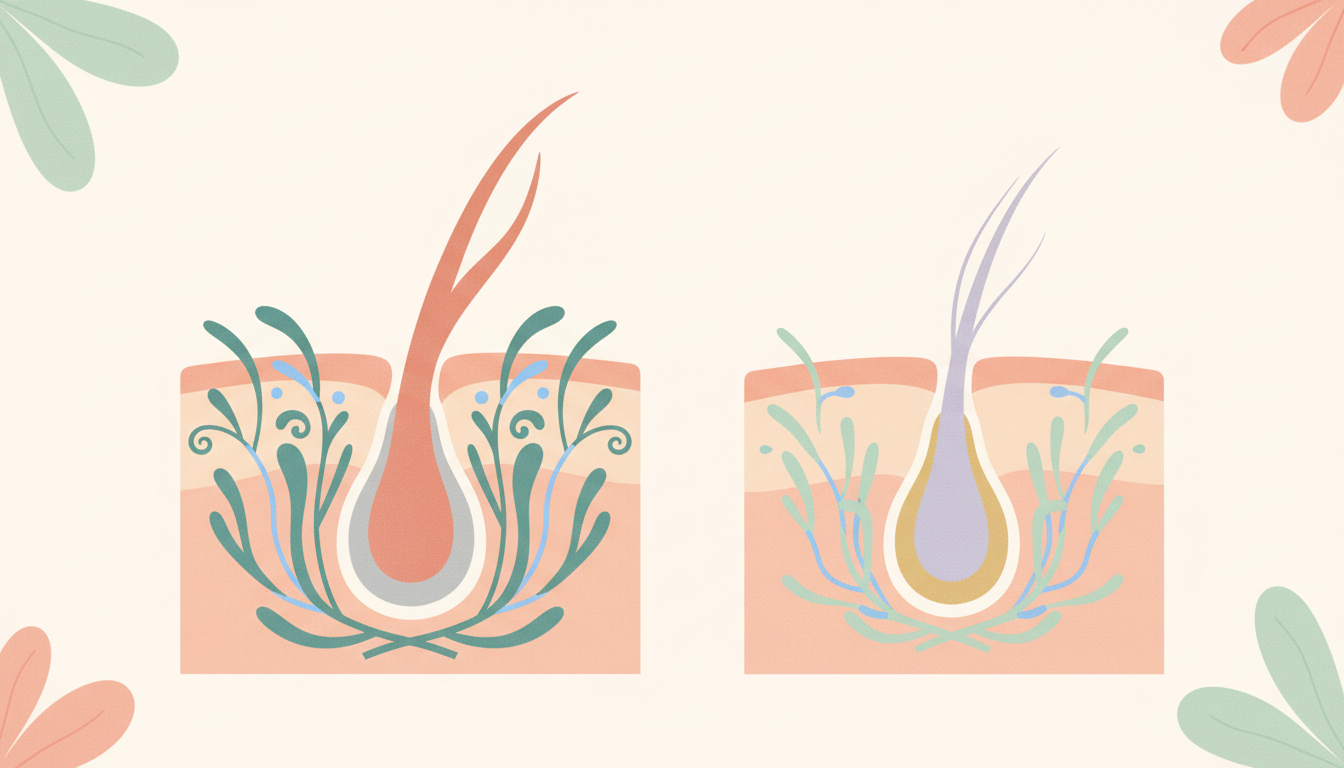
At the heart of androgenic alopecia is an androgen hormone called dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. Testosterone, a common male hormone (also present in women), is converted into DHT by an enzyme known as 5-alpha-reductase. In individuals genetically predisposed to AGA, hair follicles on the scalp are highly sensitive to DHT. When DHT binds to receptors in these follicles, it triggers a process called miniaturization. This causes hair follicles to shrink over time, producing progressively thinner, shorter, and weaker hairs, eventually leading to dormant follicles that cease producing hair altogether.
What is Saw Palmetto (Serenoa Repens)?
Saw Palmetto is a small palm tree native to the southeastern United States, primarily Florida. Its berries have been used for centuries in traditional Native American medicine for a variety of ailments, including urinary tract issues, reproductive health, and general vitality. Today, extracts from its dark berries are widely available as a dietary supplement, primarily recognized for their potential role in prostate health and, increasingly, in hair loss prevention. The active compounds in Saw Palmetto are believed to be fatty acids, sterols, and flavonoids, which contribute to its therapeutic properties.
The Proposed Mechanism: How Saw Palmetto Might Work for Hair Loss
The interest in Saw Palmetto for hair loss largely stems from its theorized ability to interfere with the same pathway that pharmaceutical drugs like finasteride target. The prevailing hypothesis is that Saw Palmetto acts as an inhibitor of the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, thereby reducing the conversion of testosterone into DHT. By lowering DHT levels, it's believed that Saw Palmetto could help protect hair follicles from miniaturization, potentially slowing down hair loss and even promoting hair regrowth.
Saw Palmetto as a Natural DHT Blocker
Specifically, Saw Palmetto is thought to inhibit both Type 1 and Type 2 5-alpha-reductase isoenzymes, although its inhibitory effect on Type 2 is generally considered stronger. Type 2 5-alpha-reductase is predominantly found in hair follicles and the prostate. By blocking this enzyme, Saw Palmetto aims to reduce the concentration of DHT in susceptible tissues, thereby potentially mitigating its adverse effects on hair follicles. This mechanism forms the scientific basis for its use in treating androgenic alopecia, positioning it as a natural alternative to prescription medications.
Saw Palmetto targets the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme to reduce DHT levels.
While the mechanism of action for Saw Palmetto in inhibiting 5-alpha-reductase is well-documented in laboratory settings and animal studies, its exact efficacy and consistent impact on human hair growth in real-world scenarios are still areas of active research and debate.
Diving into the Evidence: What Do Studies Say About Saw Palmetto and Hair Loss?
The scientific community has conducted various studies to evaluate Saw Palmetto's effectiveness for hair loss, yielding a mixed but generally cautiously optimistic picture. While some studies suggest promising results, others highlight the need for more robust, large-scale clinical trials. It's important to differentiate between anecdotal reports and scientifically validated data when assessing its potential.
Clinical Trials and Research Findings
Several smaller studies and systematic reviews have investigated Saw Palmetto for androgenic alopecia. For instance, a 2012 review of seven studies found that Saw Palmetto improved hair growth in 60% of people with AGA. Another study published in the 'International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology' showed that a topical application of Saw Palmetto extract led to a significant increase in hair density and thickness in a small group of men with AGA. Oral supplements have also been studied; a notable trial involving men with mild to moderate AGA demonstrated that twice-daily intake of 320mg of Saw Palmetto led to hair growth in 38% of participants after two years, with responders experiencing a significant increase in hair count. These results, while not universally dramatic, indicate a potential benefit for a subset of individuals.
Limitations and Inconsistencies in Research
Despite the encouraging findings, the evidence base for Saw Palmetto is not as extensive or conclusive as for FDA-approved medications like minoxidil or finasteride. Many studies are small, short-term, or lack a robust placebo control group. There's also a lack of standardization in the Saw Palmetto extracts used, which can vary widely in their active compound content, making it difficult to compare results across different studies or to recommend a precise dosage with absolute certainty. The exact mechanism by which it impacts hair growth in humans is also not fully understood, and its effect can be less potent than pharmaceutical options. Therefore, while promising, the current body of evidence suggests it may offer mild to moderate benefits for some, rather than being a universal solution.

Dosage and Administration
Given the variations in research, there isn't one universally agreed-upon standard dosage for Saw Palmetto for hair loss. However, many studies demonstrating positive effects have utilized doses ranging from 160 mg to 320 mg of extract, often taken twice daily. It's crucial to select a high-quality extract that is standardized to contain at least 85-95% fatty acids and sterols, as these are considered the primary active compounds. As with any supplement, consulting a healthcare professional before starting is advisable to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure it's safe for your individual health profile.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Profile
Saw Palmetto is generally considered well-tolerated by most people. When side effects do occur, they are typically mild and transient. Common side effects can include:
- Digestive Upset: Nausea, diarrhea, constipation, or stomach pain.
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
More serious side effects are rare but can include liver problems or increased bleeding risk, especially in individuals taking blood-thinning medications. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, and individuals with hormone-sensitive conditions should avoid Saw Palmetto. Always discuss with a doctor, especially if you are on other medications, to avoid potential interactions.
Consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Even natural supplements can interact with medications or have contraindications for certain health conditions. Professional guidance ensures safety and optimizes potential benefits.
Managing Expectations: A Realistic Outlook
While Saw Palmetto offers a natural avenue for those seeking to address hair loss, it's important to approach its use with realistic expectations. It is not a miraculous cure, nor is it likely to reverse advanced baldness. Its potential benefits are typically seen in slowing down further hair loss, maintaining existing hair, and possibly stimulating some regrowth in individuals with early to moderate androgenic alopecia. Results, if any, are usually gradual and require consistent use over several months to become apparent. It may work better for some individuals than others, reflecting the complex and individualized nature of hair loss.
Combining Saw Palmetto with Other Treatments
For many, Saw Palmetto might be considered as part of a multi-faceted approach to hair loss. It can potentially be used in conjunction with other natural supplements known to support hair health, such as biotin, zinc, and specific vitamins. Some individuals also explore combining it with conventional treatments like topical minoxidil, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. The rationale here is that different treatments may target different aspects of hair health or work through complementary mechanisms, potentially offering a more comprehensive solution. However, always consult with a dermatologist or doctor before combining treatments to ensure safety and avoid adverse interactions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Saw Palmetto for Hair Loss
Results from Saw Palmetto, if any, are typically not immediate. Most studies and anecdotal reports suggest that consistent use for at least 3 to 6 months is required before any noticeable changes in hair loss or regrowth can be observed. Patience and consistency are key.
While both Saw Palmetto and Finasteride target the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, Finasteride is a pharmaceutical drug with a stronger, more consistent, and extensively documented efficacy in clinical trials for treating androgenic alopecia. Saw Palmetto is generally considered less potent, offering milder benefits, and its evidence base, while promising, is not as robust as Finasteride's.
Yes, women with androgenic alopecia can potentially use Saw Palmetto. However, pregnant or breastfeeding women should absolutely avoid it due to its hormonal effects. For other women, consulting a doctor is essential, especially given the nuances of female pattern hair loss and potential hormonal interactions.
When choosing a Saw Palmetto supplement, look for an extract standardized to contain 85-95% fatty acids and sterols. These are believed to be the primary active ingredients responsible for its beneficial effects. A reputable brand and third-party testing can also ensure product quality and purity.
Some individuals report an initial increase in hair shedding when starting hair loss treatments, including natural supplements like Saw Palmetto. This 'shedding phase' is often considered a sign that dormant hair follicles are being stimulated and are pushing out old, weaker hairs to make way for new growth. If shedding persists or is excessive, consult a healthcare professional.
Summary: Key Takeaways on Saw Palmetto and Hair Loss
In conclusion, Saw Palmetto presents a natural option for individuals looking to address androgenic alopecia, primarily by its potential action as a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor, reducing DHT levels. Here are the key points to remember:
- Mechanism: Saw Palmetto is believed to block the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, thereby reducing the conversion of testosterone to DHT, a primary cause of androgenic alopecia.
- Evidence: While promising, the scientific evidence supporting Saw Palmetto's efficacy for hair loss is still developing. Smaller studies and reviews suggest mild to moderate benefits for some individuals, but more large-scale, rigorous trials are needed.
- Expectations: It is not a miracle cure and should be approached with realistic expectations. Results are typically gradual and may include slowing hair loss, maintaining existing hair, or promoting modest regrowth.
- Safety: Generally well-tolerated with mild side effects like digestive upset. However, certain groups (pregnant/breastfeeding women, those on specific medications) should avoid it.
- Dosage: Look for standardized extracts (85-95% fatty acids and sterols). Doses around 160-320 mg twice daily have been used in studies, but consultation with a doctor is advised.
- Integration: Can be considered as part of a broader hair care regimen, possibly alongside other supplements or conventional treatments under medical supervision.
Ultimately, Saw Palmetto offers a compelling natural choice for some, particularly those seeking alternatives or adjuncts to pharmaceutical options. As with any health intervention, individual responses can vary, and consulting a healthcare provider is always the best first step.