The "Zombie Fungus" Mystery: Unraveling Cordyceps' Journey from Insect to Human Ally
The "Zombie Fungus" Mystery: Unraveling Cordyceps' Journey from Insect to Human Ally

Cordyceps, often sensationalized as the 'zombie fungus,' is a fascinating and complex organism that has garnered significant attention from both nature enthusiasts and the scientific community. This article delves into the extraordinary life cycle of Cordyceps, explaining how it masterfully manipulates insect hosts, and then transitions to explore its surprising and well-documented benefits for human health, including its role as a potent adaptogen known to support energy levels, enhance athletic performance, and bolster the immune system. We will also examine its historical significance, the science behind its therapeutic properties, and the shift from rare wild harvesting to sustainable cultivation, particularly of Cordyceps militaris.
The Enigmatic Life Cycle of Cordyceps
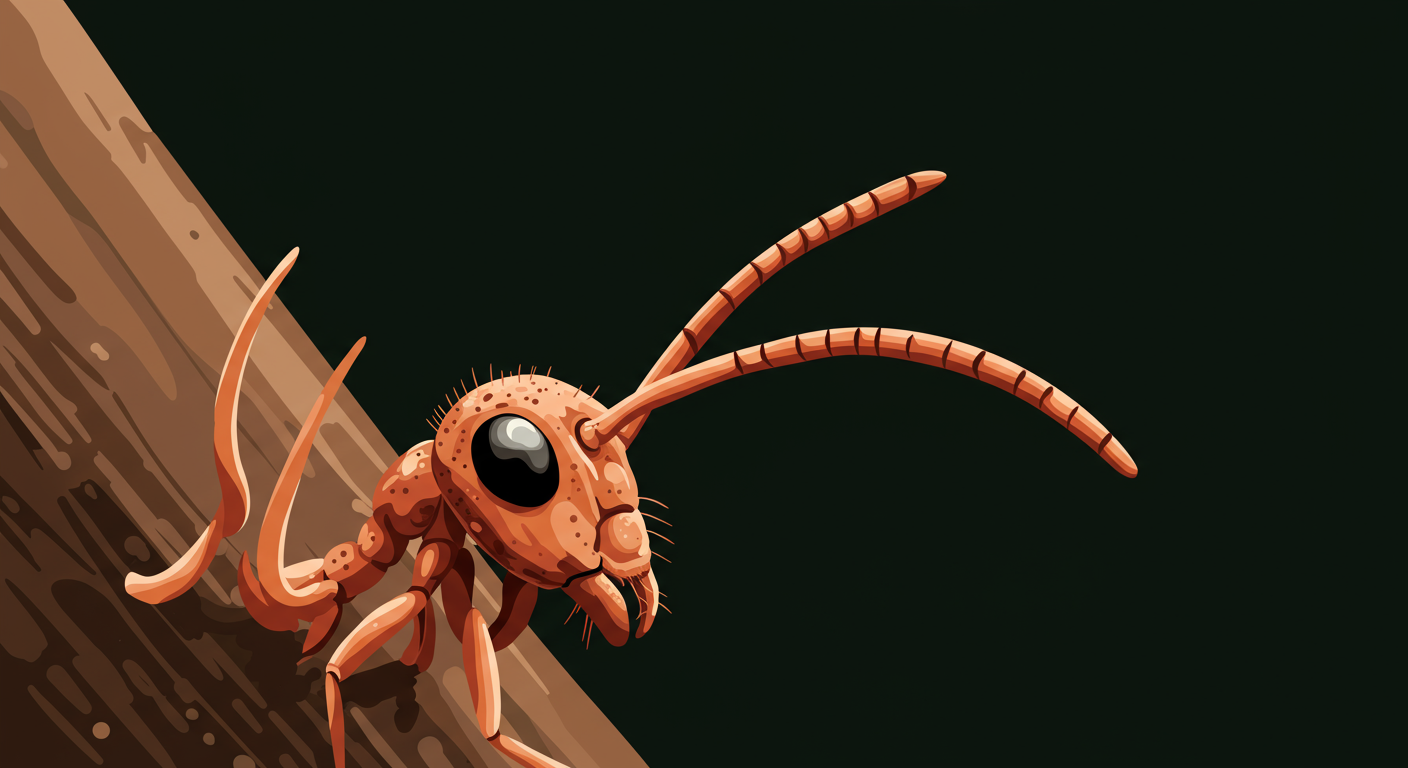
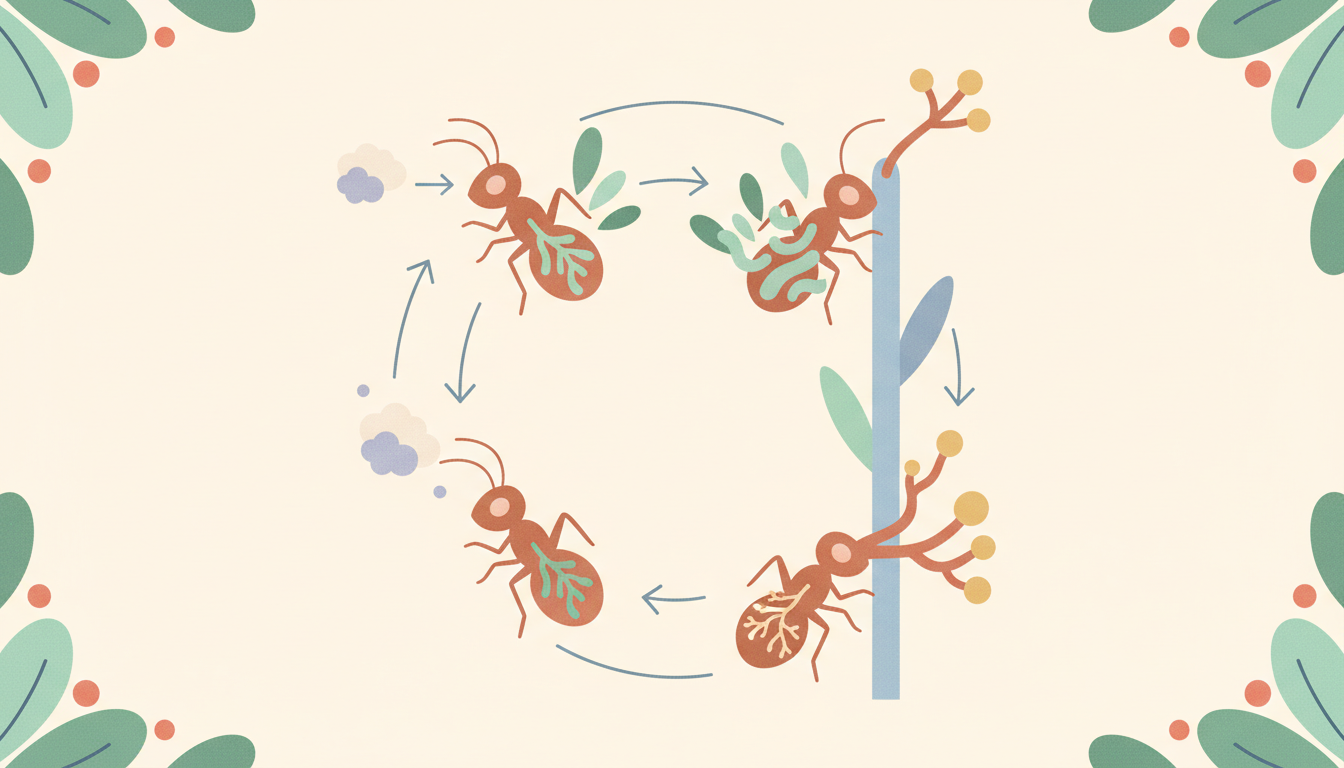
The most striking aspect of Cordyceps is undoubtedly its parasitic life cycle, a spectacle of nature that has earned it the moniker 'zombie fungus.' This phenomenon, while unsettling, is a testament to the sophisticated evolutionary strategies fungi employ. The journey begins when microscopic Cordyceps spores, released from mature fungal bodies, come into contact with a susceptible insect, such as an ant or caterpillar. Once attached, the spore penetrates the insect's exoskeleton, marking the start of an internal takeover.
Inside the host, the fungus begins to grow, slowly consuming the insect's non-vital tissues. What truly sets Cordyceps apart is its ability to manipulate the host's behavior. As the fungus matures, it releases neurotoxins and other compounds that alter the insect's neurological functions, compelling it to leave its colony or usual habitat. The infected insect is often driven to climb to a high vantage point, like a tall blade of grass or a tree branch, where it clamps on with its mandibles, becoming immobilized.
This strategic positioning is crucial for the fungus's reproductive success. Once the insect is secured in an elevated and humid spot, the Cordyceps fungus erupts from its head or other parts of its body, forming a fruiting body. This stalk-like structure is designed to release new spores, which are then carried by the wind, maximizing their dispersal and increasing the chances of infecting new hosts. This entire process, from infection to sporulation, highlights a remarkable example of co-evolution between parasite and host.
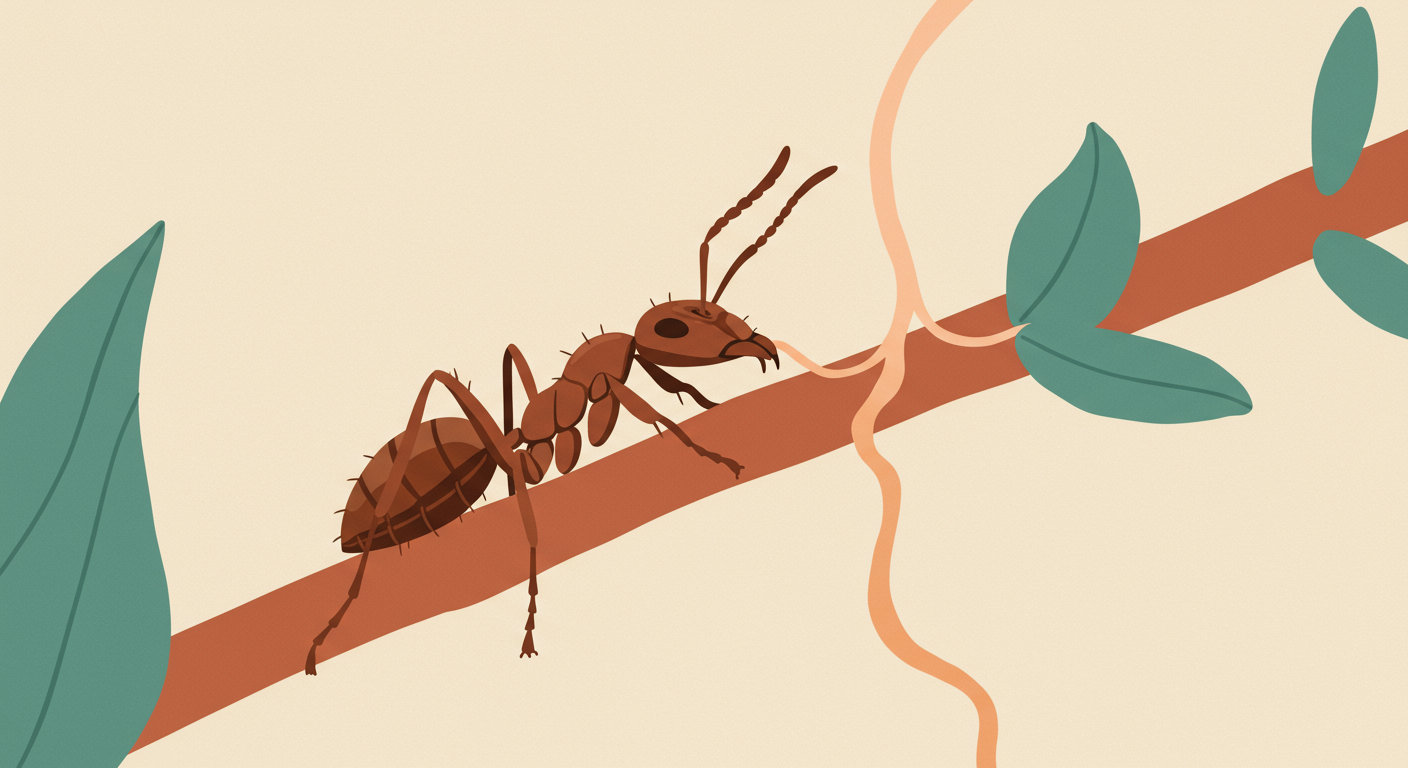

The term "zombie fungus" became widely known through documentaries and fictional works, highlighting Cordyceps' unique ability to control its insect hosts for reproductive advantage. While fascinating, it's crucial to remember this effect is specific to insects and poses no threat to human consciousness or behavior.
From Forest Floor to Modern Pharmacy: Cordyceps for Human Health
Despite its dramatic origins, Cordyceps has long been revered in traditional Eastern medicine for its profound health-promoting properties. Far from turning humans into mind-controlled hosts, this fungus offers a wealth of benefits, primarily acting as a powerful adaptogen. Adaptogens are natural substances that help the body adapt to various stressors, promoting balance and resilience. Cordyceps helps modulate the body's physiological response to stress, supporting overall vitality and well-being.
Historical texts from China and Tibet have documented its use for centuries, particularly for enhancing physical stamina, reducing fatigue, and supporting respiratory health. Modern scientific inquiry has begun to validate many of these traditional uses, identifying key bioactive compounds responsible for its therapeutic effects. Its journey from a mysterious forest dweller to a celebrated dietary supplement underscores nature's intricate ability to provide solutions for human health.
Boosting Energy and Athletic Performance
One of the most celebrated benefits of Cordyceps is its potential to naturally boost energy levels and enhance athletic performance. This effect is largely attributed to its ability to support the body's production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. By increasing ATP synthesis, Cordyceps may improve oxygen utilization and stamina, allowing individuals to exercise longer and recover more efficiently. Studies have shown improvements in exercise capacity and endurance in various populations, suggesting its utility for athletes and those seeking an energy uplift.
Beyond just providing a quick energy surge, Cordyceps works at a foundational level, helping the body to generate energy more effectively. This can translate into reduced fatigue, greater endurance, and an overall feeling of sustained vitality, making it a popular choice for those looking to optimize their physical capabilities without relying on stimulants.
Fortifying the Immune System
Cordyceps is also recognized for its significant immune-modulating properties. It contains polysaccharides, nucleosides, and other compounds that can stimulate or suppress different aspects of the immune system, helping to maintain balance. This adaptogenic action means it can help fortify the body's natural defenses against pathogens while also potentially regulating overactive immune responses. It's not about hyper-stimulating the immune system, but rather optimizing its function so it can respond effectively when needed.
Regular supplementation with Cordyceps may help the body become more resilient to common illnesses and support recovery. This makes it a valuable addition to the regimen of anyone looking to enhance their overall immune health and maintain well-being throughout the year.

The Science Behind the Fungus: Key Bioactive Compounds
The remarkable health benefits of Cordyceps are not mere folklore; they are increasingly supported by scientific research focusing on its diverse array of bioactive compounds. Among the most prominent is Cordycepin, a nucleoside analog that has shown promise in various studies for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potentially anti-cancer properties. Cordycepin is thought to be a key player in the fungus's ability to enhance ATP production and exert immune-modulating effects.
Beyond Cordycepin, Cordyceps is rich in other beneficial compounds including polysaccharides, which are complex carbohydrates known for their immune-boosting and anti-tumor effects; adenosine, a nucleoside that plays a crucial role in cellular energy transfer and cardiovascular health; and various triterpenes and sterols. These compounds work synergistically, contributing to the holistic adaptogenic effects observed with Cordyceps consumption. Research continues to uncover the full spectrum of their actions and potential therapeutic applications.
Modern scientific studies are continually exploring the mechanisms by which Cordyceps exerts its health benefits. While promising, it's important to note that many studies are preclinical or require larger human trials to establish definitive clinical efficacy and recommended dosages for specific health conditions.
Wild vs. Cultivated: Sourcing Cordyceps Responsibly
Historically, wild Cordyceps, particularly Ophiocordyceps sinensis (often referred to simply as Cordyceps sinensis), was an exceptionally rare and highly prized commodity. Found predominantly in the high-altitude regions of the Himalayan plateau, it was collected by hand from mummified insect larvae, making it one of the most expensive natural medicines in the world. Its scarcity led to concerns about overharvesting and environmental impact, driving prices sky-high and making it inaccessible for most.
Fortunately, advancements in mycology have led to the successful cultivation of other Cordyceps species, primarily Cordyceps militaris. This cultivated variety is grown on substrates like grain or rice in controlled laboratory environments, offering a sustainable and ethical alternative to wild harvesting. Crucially, cultivated Cordyceps militaris has been shown to contain similar, if not higher, concentrations of many beneficial compounds, including Cordycepin, compared to its wild counterpart. This makes it a viable and accessible option for obtaining the health benefits of Cordyceps without compromising ecological balance.
Understanding Dosage and Safety
When considering Cordyceps supplementation, it is important to understand that while generally well-tolerated, individual responses can vary. Most Cordyceps supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, powders, and extracts, often derived from Cordyceps militaris fruiting bodies or mycelial biomass. Standard dosages typically range from 1 to 3 grams per day, but this can depend on the concentration of active compounds in the specific product and the intended health goal.
As with any supplement, consulting a healthcare professional before starting Cordyceps is advisable, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions, those taking medications, or pregnant/nursing women. While side effects are rare, they can include mild digestive upset. Choosing reputable brands that provide third-party testing for purity and potency is also key to ensuring you receive a high-quality, effective product.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cordyceps
No, absolutely not. The 'zombie fungus' effect of Cordyceps is specific to certain insects and is a result of complex biological interactions unique to those hosts. Humans lack the necessary biological pathways for Cordyceps to exert such control, and consuming Cordyceps supplements poses no risk of mind manipulation.
Wild Cordyceps (primarily Ophiocordyceps sinensis) is found on insect larvae in specific high-altitude regions and is extremely rare and expensive. Cultivated Cordyceps (mostly Cordyceps militaris) is grown in controlled environments and offers similar, often higher, concentrations of beneficial compounds like Cordycepin. Cultivated varieties are a sustainable and more accessible alternative.
The time it takes to experience benefits can vary greatly among individuals and depends on factors such as dosage, consistency of use, and individual metabolism. Some people report feeling subtle energy or endurance improvements within a few weeks, while others may require longer, sustained use to notice more significant effects, particularly for immune support.
Cordyceps is generally considered safe for most healthy adults when taken at recommended dosages. Mild side effects such as digestive upset (e.g., diarrhea, constipation, nausea) have been reported but are rare. Individuals with autoimmune conditions, bleeding disorders, or those taking immunosuppressants or blood thinners should consult a healthcare professional before use due to potential interactions or effects on the immune system.
Cordycepin is one of the most studied bioactive compounds found in Cordyceps. It is a nucleoside analog that has been researched for its potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immune-modulating, and even anti-tumor properties. It is believed to contribute significantly to Cordyceps' ability to enhance ATP production and support overall cellular health, making it a key indicator of supplement quality.
Summary: Cordyceps - A Remarkable Fungal Ally
Cordyceps is truly one of nature's most intriguing organisms, bridging the gap between a captivating biological phenomenon and a powerful natural health ally. Its journey from insect manipulator to human adaptogen is a testament to the complex biochemistry found in the natural world. Here are the key takeaways from our exploration:
- Parasitic Master: Cordyceps is famously known as the 'zombie fungus' for its unique ability to infect and control insect hosts, compelling them to climb to high vantage points before sprouting a fungal body for spore dispersal.
- Human Ally: Despite its origins, Cordyceps offers a wide array of health benefits for humans, acting primarily as an adaptogen that helps the body cope with stress and maintain balance.
- Energy & Performance: It is highly valued for its potential to enhance energy levels, improve oxygen utilization, and boost athletic performance by supporting ATP production.
- Immune Support: Cordyceps possesses significant immune-modulating properties, helping to fortify the body's natural defenses and regulate immune responses.
- Bioactive Compounds: Its therapeutic effects are attributed to key compounds like Cordycepin, polysaccharides, and adenosine, which work synergistically.
- Sustainable Sourcing: While wild Cordyceps (Ophiocordyceps sinensis) is rare and expensive, cultivated varieties like Cordyceps militaris offer a sustainable and equally potent source of these beneficial compounds.
- Not a Zombie Threat: The 'zombie' effect is exclusive to insects and does not transfer to humans; Cordyceps is safe for human consumption as a supplement.
- Consult Professionals: Always consult a healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are on medication.